Clostridium Bacteria Stain Which Color Using the Gram Stain
Gram staining divides bacteria into two categories as gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria. Slim Gram-positive bacilli with round terminal spores a drumstick appearance.

Gram S Staining X100 1 Sub Terminal Spore 2 Central Spore 3 Thick Download Scientific Diagram
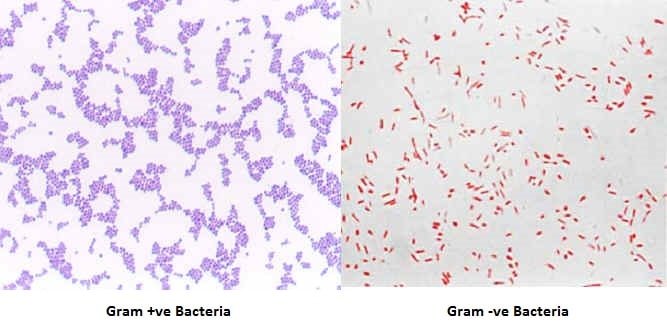
After successful gram staining gram-positive bacteria appear purple and gram-negative bacteria will appear reddish-pink.
. Gram stains may also be used to check for bacteria in certain body fluids such as blood or urine. Cocci will be unstained Simple stain - the spores inside look clear and the cells just have the stain. Identification of anaerobes recovered from clinical samples is complicated by the fact that certain gram-positive anaerobes routinely stain gram negative.
Arranged in chains pairs singles Disease they cause. It is pink after being stainred. Gram - stain.
There is also a Gram-variable which carries the color purple in the Gram stain with very few duplicates of the Gram stain. Gram positive bacteria stain violet due to the presence of a thick layer of peptidoglycan in their cell walls which retains the crystal violet these cells are stained with. Gram-positive bacteria have a thick mesh-like cell wall made of peptidoglycan 50-90 of cell wall which stains purple while Gram-negative bacteria have a thinner layer 10.
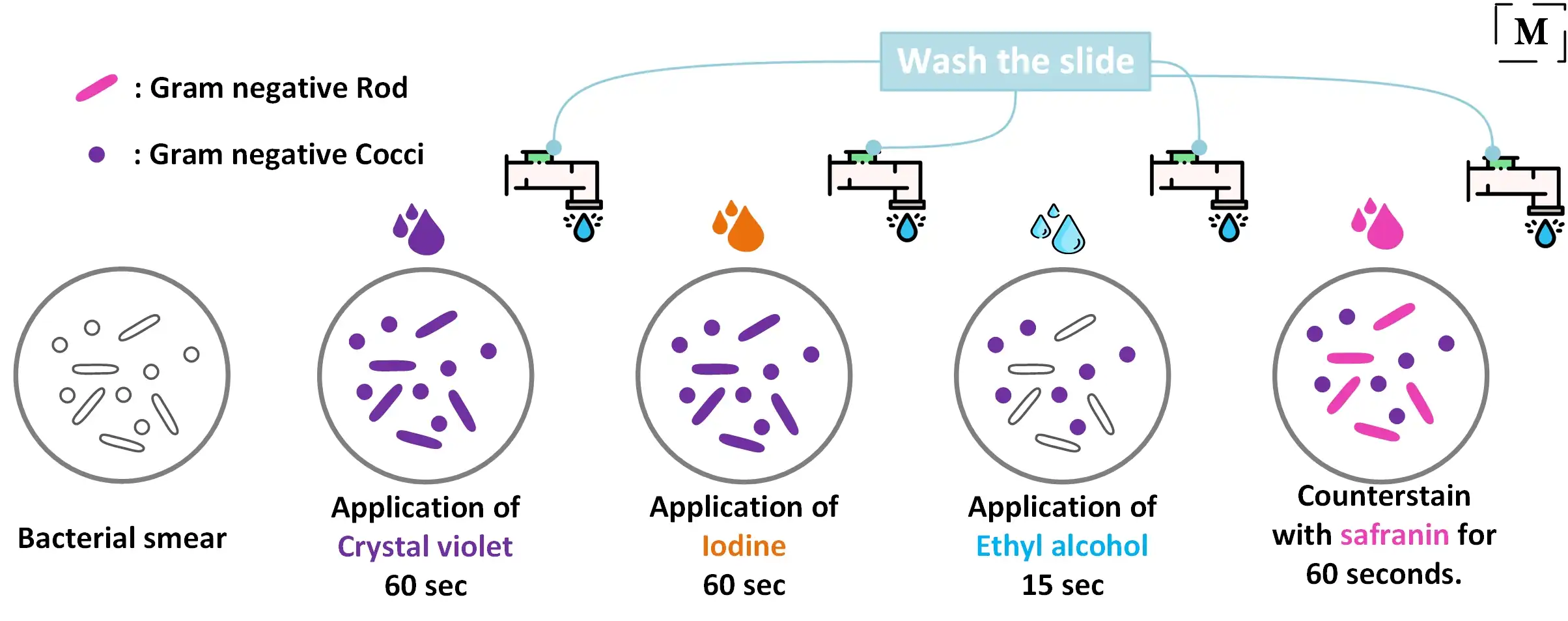
Health professionals need to understand the important difference between gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Gram-positive bacteria have a thick mesh-like cell wall made of peptidoglycan 5090 of cell envelope and as a result are stained purple by crystal violet whereas gram-negative bacteria have a thinner layer 10 of cell envelope so do not retain the purple stain and are counter-stained pink by safranin. There is a stain on them purple because of their color.
Gram positive vs gram negative bacteria diagram showing the color difference after gram staining. In this figure The gram-positive bacteria stain dark blue or purple while the gram-negative bacteria stain pink. Why is Gram staining important.
Gram-positive bacteria will appear purple or blue while gram-negative bacteria will appear red or pink. Gram-positive bacteria have a thick mesh-like cell wall made of peptidoglycan 5090 of cell envelope and as a result are stained purple by crystal violet whereas gram-negative bacteria have a thinner layer 10 of cell envelope so do not retain the purple stain and are counter-stained pink by the Safranin Fuchsine. May be predominantly Gram-negative in very young or old cultures.
Which of the following correctly describe how the Gram stain works to color different types of cells. Despite their weight 80 of a cell gram-positive bacteria have thick layers of peptidoglycan. Using the Gram stain procedure the cells of B.
Clostridium tetani look very clean large and dark colored on a gram stain. The diagram above shows a comparison of gram positive vs gram negative bacteria under microscope. There are two main categories of bacterial infections.
Gram-negative bacteria are decolorized by the alcohol losing the color of the primary stain purple. Gram positive rod Color. A Gram stain is a test that checks for bacteria at the site of a suspected infection such as the throat lungs genitals or in skin wounds.
Bacteria found in colonies with positive bacteria have walls made of peptidoglycan-releasing polymers 10 percent and lipids over 80 percent. After decolorization step a counterstain is used to impart a pink color to the decolorized gram-negative organisms. At the completion of the Gram Stain gram-negative bacteria will stain pinkred and gram-positive bacteria will stain bluepurple.
Two clinically significant genera of bacteria that are capable of. The main benefit of a gram stain is that it helps your doctor learn if you have a bacterial infection and it determines what type of bacteria are causing it. Hans Christian Gram developed the staining method in 1884.
Place these reagents in the proper order of their use in the Gram staining technique. They look like this because of the way the light from the sun hits them when on a gram stain. Some will be purple and pink rods.
Most com- monly seen with Bacillus spp Infections with Clostridium spp. Acineto- bacillus is a. The cells with clear components are endospore formers because this method of staining does not penetrate through the endospores.
The schaeffer - fulton method does that. - bacteria microscopy - Sporulating Clostridium tetani micrograph. Gram-positive bacteria are bacteria classified by the color they turn in the staining method.
Such as those caused by Clostridium f Clostridium spp. Most com- monly seen with Bacillus spp Clostridium spp Acineto- bacter spp Streptococcus pneumoniae. Gram-positive bacteria are not decolorized by alcohol and will remain as purple.
Bacteria that partially retain the purple color of the crystal violet in the Gram stain. Subtilis would appear purple because they have a thick layer of peptidoglycan in their cell wall. The most common shapes include round cocci or rod-shaped bacilli.
Using a Brightfield microscope. Bacteria can be differentiated by the thickness of the peptidoglycan layer using a specialized stain called a Gram stain. Principal of Gram staining.
Peptostreptococcus asaccharolyticus Eubacterium plautii Clostridium ramosum Clostridium symbiosum and Clostridium clostridiiforme are among the nonconformists with regard to conventional Gram-staining. In the gram staining procedure bacteria are first stained with the primary stain crystal violet. Typically bacteria that are gram-positive appear purple to blue and bacteria that are Gram-negative appear pink to red.
The staining method uses crystal violet dye which is retained by the thick peptidoglycan cell. The diseases caused by clostridium are Botulism Clostridioides Gastroenteritis Soft-tissue infections Tetanus Clostridial necrotizing enteritis Neutropenic enterocolitis. It also occurs in more bacteria with ly retain the purple color of the crystal violet in the Gram stain.
This can help your. Click to see full answer.

Gram Stain Of Clostridium Tertium Which Is An Anaerobic Motile Download Scientific Diagram

Gram Stained Smear Of Pure Culture Of Clostridium Perfringens Showing Download Scientific Diagram

Gram Positive Vs Gram Negative Technology Networks

What Is The Gram Stain Of Clostridium Botulinum Clostridium Botulinum Stain Lettering

B Cereus Positive Gram Stain Bacteria แบคท เร ย Bacillus
Gram Staining Principle Procedure Interpretation Examples And Animation

Caracteristicas Microscopicas Bacilos Grampositivos Esporoformadores Inmovil Medical Laboratory Scientist Medical Laboratory Science Medical Laboratory

Gram Staining Of Gram Positive C Sporogenes Dsm 795 Scale Bar Download Scientific Diagram
Gram Staining Principle Procedure Interpretation Tips

Bacteria 101 Cell Walls Gram Staining Common Pathogens Tusom Pharmwiki

Gram Stain Of Clostridium Symbiosum Showed Gram Negative Rod Shaped Download Scientific Diagram

Gram Stain Qc Bacteria Bacteria Art Science Science Art Microscope Science Gift Bacillus Medical Print Watercolor Science Print Science Art Biology Art Science Gifts

Gram Stain Mixed Culture Gram Positive Cocci Gram Negative Rod Microbiology Gram Negative Bacteria Medical Laboratory Science

Gram Positive Bacteria Examples And Structure Jotscroll

Clostridium Gram Stain Introduction Requirements Procedure Result

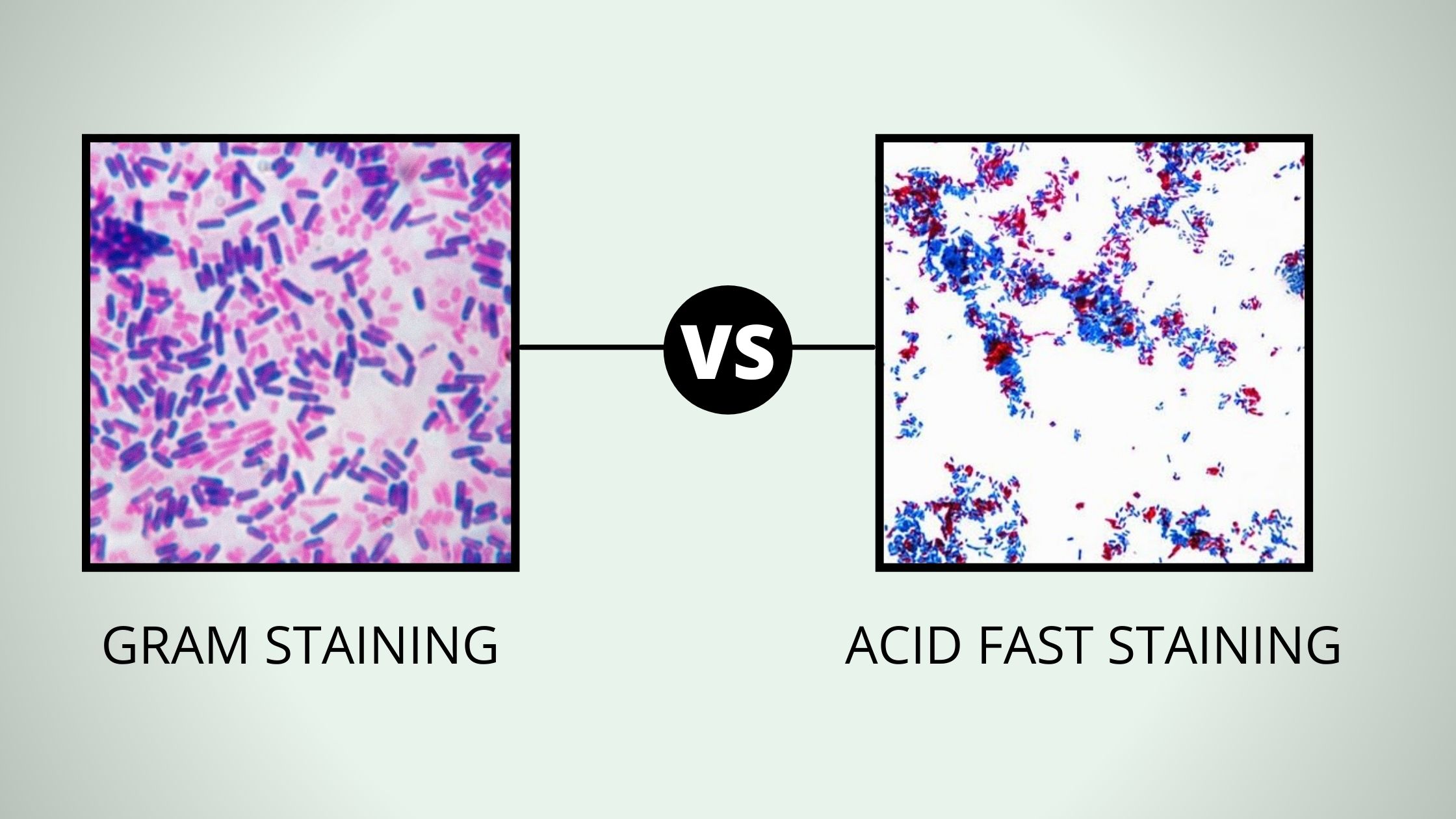
Comparison Between Gram Stain And Acid Fast

Day 243 Bacillus Cereus Microbiology Protists Bacillus

Gram Positive Bacteria Bacillus Clostridium Nocardia Actinomyces Bacillus Septicemia Positivity

Comments
Post a Comment